Semaphore的使用及原理
Semaphore(信号量)是一种线程同步机制,用于控制同时访问共享资源的线程数量。它维护了一个许可集,在许可可用时允许访问共享资源,并在许可被使用时阻塞访问请求。
考虑这样一种场景:我们有n个礼物,有m个窗口,每个窗口都可以单独售卖礼物,礼物卖完即止。
在这个场景里,一方面要对礼物数量进行线程安全控制,防止商品超卖;另外一方面,可以通过Semaphore控制窗口的数量。
首先解决商品超卖的问题,这里通过GiftManager进行商品的数量管理,实际应用的时候,往往需要与数据库进行交互。addGiftCount和removeGiftCount通过synchronized进行同步。
getInstance方法是一种单例模式,对外部只提供一个GiftManager的对象实例。
虽然含有getGiftCount方法,但是在多线程情况下,获取到的商品数量,在之后进行操作时可能都不是准确的。具体来说,当在t1时刻获取到了数量,在t2时刻进行数量阈值判断的时候,t2时刻的商品数量可能就和t1时刻的不相同。这也是在removeGiftCount中进行数量不能小于等于零的判断的原因。
@Slf4j
public final class GiftManager {
private static GiftManager instance;
private int giftCount;
private GiftManager() {
}
public synchronized void addGiftCount(int giftCount) {
this.giftCount += giftCount;
log.info("当前礼物数量为:{}", this.giftCount);
}
public synchronized boolean removeGiftCount(int giftCount) {
if (this.giftCount <= 0) {
return false;
}
this.giftCount -= giftCount;
return true;
}
public int getGiftCount() {
return giftCount;
}
/**
* 获取单例
*/
public static GiftManager getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (GiftManager.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new GiftManager();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
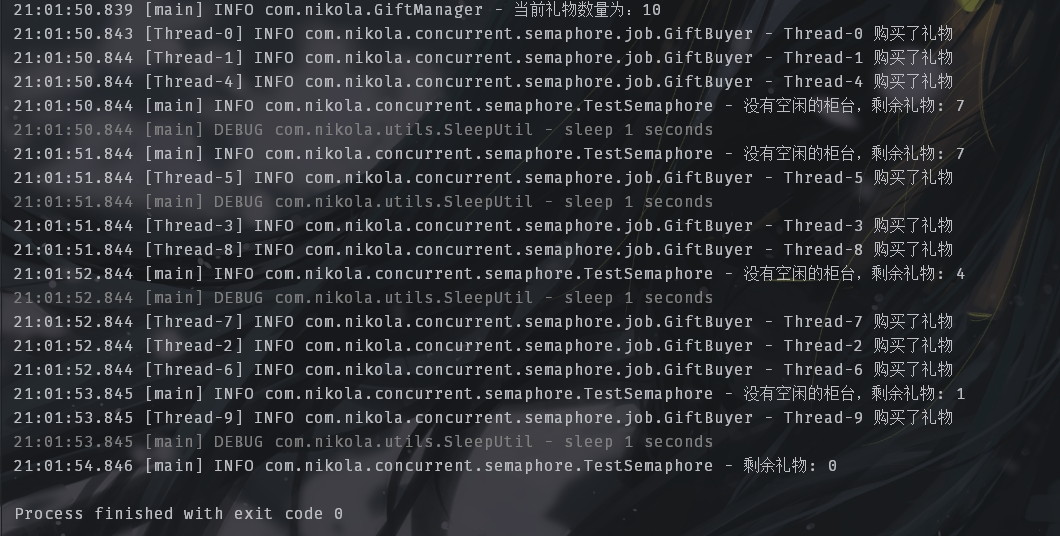
商品数量管控好之后,下面的程序用于进行商品的销售。在销售之前我们通过GiftManager添加指定数量的商品。再通过实例化Semaphore将柜台数作为信号量,用于控制并发的线程数量。只要商品数量一直大于0,柜台就可以不断卖出。为了避免不断循环创建线程,在信号量均被占用的情况下,让主线程休眠1s后再继续。
@Slf4j
public class TestSemaphore {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 礼物数量
int giftCount = 1;
// 柜台数量
int windowCount = 100;
GiftManager giftManager = GiftManager.getInstance();
giftManager.addGiftCount(giftCount);
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(windowCount);
// 只要礼物存在就可以一直卖
while (giftManager.getGiftCount() > 0) {
if (semaphore.availablePermits() == 0) {
log.info("没有空闲的柜台,剩余礼物: {}", giftManager.getGiftCount());
SleepUtil.sleep(1);
continue;
}
new Thread(new GiftBuyer(semaphore)).start();
}
log.info("剩余礼物: {}", giftManager.getGiftCount());
}
}
运行结果:
- 商品数:1,柜台数:100:
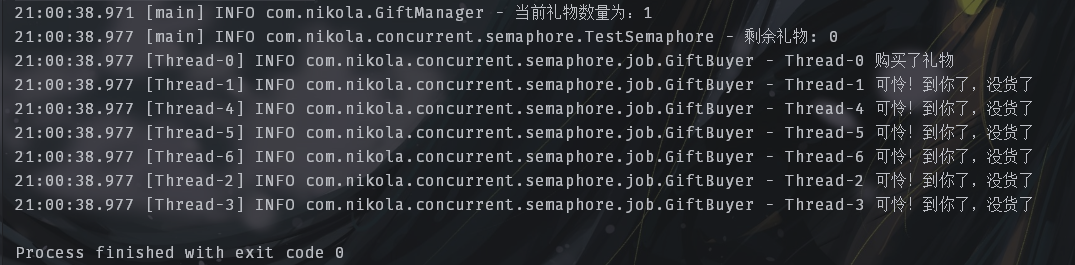
2. 商品数:10,柜台数:3:
原理
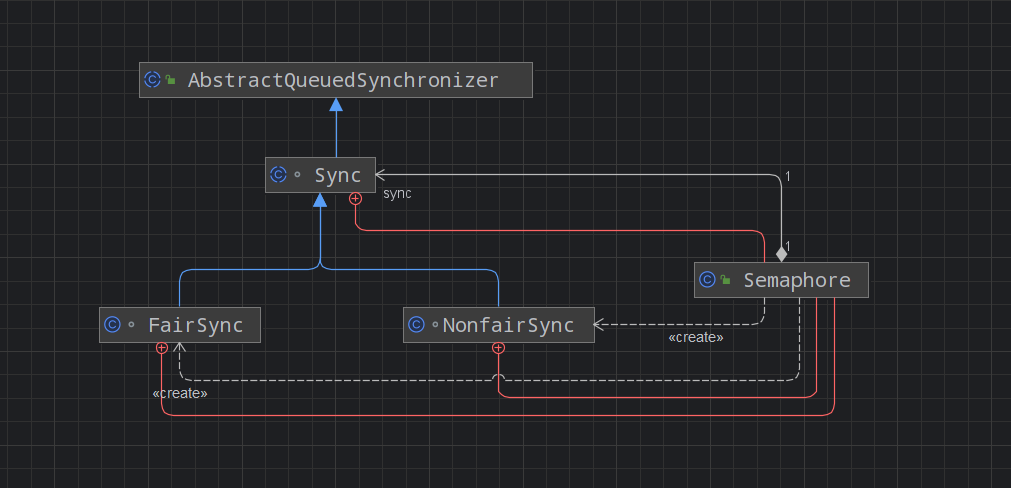
Semaphore的类关系图如下,含有3个内部类Sync、FairSync、NonfairSync,这3个都是同步器,后面两个是前者的子类,分别表示公平同步器、非公平同步器。Sync是基于AbstractQueuedSynchronizer实现的。
Sync
Sync是Semaphore的内部同步器类,继承自AQS。它(AQS)维护了一个状态变量state,该参数可以通过实例化Semaphore时通过指定许可数进行设置。
nonfairTryAcquireShared
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
nonfairTryAcquireShared方法用于非公平获取许可,直接尝试CAS修改state,如果state大于等于0则获取许可成功,否则加入等待。
compareAndSetState方法的作用是使用CAS原子操作尝试将state从available修改为remaining,如果修改成功则代表获取许可成功,否则失败。失败的情况下会在循环不断重试,直到修改成功。所以,这种许可的获取方式是非公平的。
tryReleaseShared
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current + releases;
// next < current表示计数超出上限(`Integer.MAX_VALUE`)的情况
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
tryReleaseShared方法用于尝试释放许可,使用CAS将state从remaining修改回available。如果修改成功代表释放许可成功。
reducePermits与drainPermits
reducePermits与drainPermits方法用于减少或清空许可数。逻辑基本同上。
final void reducePermits(int reductions) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current - reductions;
if (next > current) // underflow
throw new Error("Permit count underflow");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return;
}
}
final int drainPermits() {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
if (current == 0 || compareAndSetState(current, 0))
return current;
}
}
NonfairSync
NonfairSync非公平同步器的代码:
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L;
NonfairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
}
可以看到它提供了一个获取许可的方法tryAcquireShared,该方法调用了父类Sync的nonfairTryAcquireShared方法,通过非公平的方式获取许可。
FairSync
FairSync公平同步器的代码:
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2014338818796000944L;
FairSync(int permits) {
super(permits);
}
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
if (hasQueuedPredecessors())
return -1;
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
}
在公平同步器中同样提供了tryAcquireShared方法,不同之处在于它会先判断当前线程是否有等待的前驱节点,如果有的话直接返回-1,否则再尝试CAS修改state获取许可。
hasQueuedPredecessors()代码为:
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
// The correctness of this depends on head being initialized
// before tail and on head.next being accurate if the current
// thread is first in queue.
Node t = tail; // Read fields in reverse initialization order
Node h = head;
Node s;
return h != t &&
((s = h.next) == null || s.thread != Thread.currentThread());
}
如果当前线程之前有队列线程,则为true;如果当前线程位于队列头部或队列为空,则为false。也就是只有当前线程是头节点的时候,才可以获取许可,从而实现了公平同步。
Semaphore的构造器
public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits);
}
Semaphore实例化时需要指定许可数(permits),当信号量>0时,可以获取许可,否则线程阻塞。
也可以设置是否公平同步器(fair),该参数为true表示使用公平同步器(FairSync)否则使用非公平同步器(NonfairSync)。
实例化时指定许可数,实际是设置Sync同步器的状态state。
获取许可
acquire()方法用于申请许可,如果没有许可,则线程会一直阻塞,直到有空闲许可,或者线程被中断。如果获取到许可,方法会立即返回,并且将可用的许可数减一。
释放许可
release方法用于释放许可(可以多个)。





