装饰器模式
About 3 min
装饰器模式,可以在不修改对象外观和功能的情况下添加或者删除对象功能。它可以使用一种对客户端来说是透明的方法来修改对象的功能,也就是使用初始类的子类实例对初始对象进行授权。
装饰器模式来为对象动态地添加了额外的责任,这样就在不使用静态继承的情况下,为修改对象功能提供了灵活的选择。
主要角色
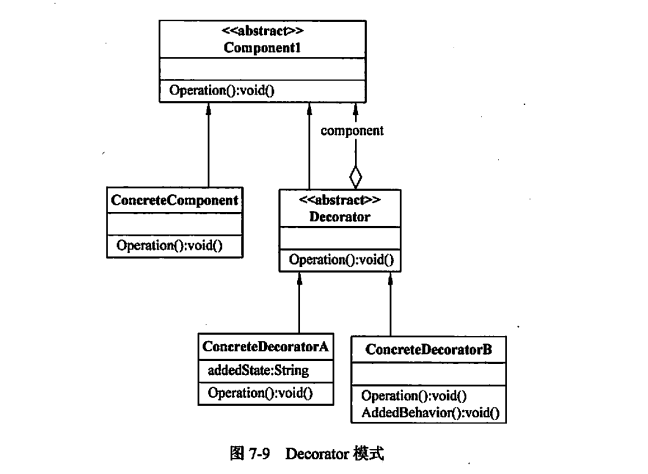
抽象构件(Component):
这是一个接口或抽象类,它定义了被装饰对象的接口。客户端通常通过这个接口与具体的实现类交互。具体构件(ConcreteComponent):
实现了抽象构件接口的具体对象,它是原始对象,具有核心业务功能。装饰器可以用于增强或修改具体构件的行为。抽象装饰(Decorator):
继承自抽象构件,实现了抽象构件的所有方法,并且包含一个指向抽象构件类型的引用,这样就可以在内部持有一个具体构件实例。
抽象装饰为具体装饰器提供了一个统一的接口扩展点,允许在运行时动态地向具体构件添加新的职责或行为。具体装饰(ConcreteDecorator):
是抽象装饰类的子类,除了重写并实现抽象装饰中的方法外,还可以在其基础上增加额外的功能。
具体装饰器可以在调用其持有的具体构件的方法时,先执行自己的附加操作,然后将控制权传递给被装饰的对象,从而达到在不修改原有类的基础上动态扩展功能的目的。
代码实现
抽象构件
public abstract class Component {
public abstract void operation();
}
具体构件
具体构件是抽象构件的实现,它里面的实现是最原始的逻辑。
public class ConcreteComponent extends Component {
@Override
public void operation() {
System.out.println("Concrete component operation");
}
}
抽象装饰器
写抽象装饰器,需要注意两个地方:
- 需要聚合原始构件。(以便进行行为扩展)
- 需要继承抽象构件。(装饰器首先是抽象构件的子类,这样行为才是一直的。只是它的实现可以是另外一种子构件,也可以是扩展其持有的子构件的行为)
public abstract class Decorator extends Component {
private Component component;
public Decorator(Component component) {
this.component = component;
}
public Component getComponent() {
return component;
}
public void setComponent(Component component) {
this.component = component;
}
}
具体装饰器
具体装饰器,由于持有具体构件的对象,并且它也是抽象构件的子类,因此一方面它可以扩展具体构件的功能,另一方面也可以重写具体构件。
ConcreteDecoratorA是一个扩展的例子。
public class ConcreteDecoratorA extends Decorator {
private String addedState;
public ConcreteDecoratorA(Component component) {
super(component);
}
@Override
public void operation() {
this.addedState = "added";
Component component = super.getComponent();
if (component != null) {
component.operation();
}
System.out.println("state added");
}
}
ConcreteDecoratorB是一个重写的例子。
public class ConcreteDecoratorB extends Decorator {
public ConcreteDecoratorB(Component component) {
super(component);
}
@Override
public void operation() {
this.addedBehavior();
}
public void addedBehavior() {
System.out.println("Added behavior B");
}
}
调用
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component component = new ConcreteComponent();
Decorator decoratorA = new ConcreteDecoratorA(component);
Decorator decoratorB = new ConcreteDecoratorB(component);
component.operation();
System.out.println("========");
decoratorA.operation();
System.out.println("========");
decoratorB.operation();
}
}
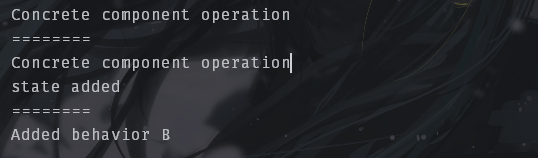
结果如下: