Sql映射文件解析
之前谈到配置文件解析的mappers节点时, 说到两种解析方式即:
MapperAnnotationBuilder用于解析package配置方式指定的接口类XMLMapperBuilder用于解析mapper配置方式指定的xml
本文详细介绍这两种方式的解析方法
MapperAnnotationBuilder
构造器
MapperAnnotationBuilder的实例化需要指定Configuration, 以及当前解析的类Class<?> type.
MapperBuilderAssistant中包含了通过configuration配置类中获取的别名注册器TypeAliasRegistry, 以及类型转换注册器TypeHandlerRegistry. 之后会用于处理mapper中的别名以及转换器配置.
public MapperAnnotationBuilder(Configuration configuration, Class<?> type) {
String resource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".java (best guess)";
this.assistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.configuration = configuration;
this.type = type;
}
MapperAnnotationBuilder的parse方法
parse方法的具体逻辑见下, 注释是方法中各个步骤的含义
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
// 判断是否已经解析了当前的resource, resource即类全限定名(含有前缀interface or class or 空字符(对于原始类型))
// 已经解析过的类的全限定名会存放到`Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<>()`中.
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 通常我们的接口会对应一个xml文件, `loadXmlResource()`就是用于获取该xml文件并进行解析的方法.
loadXmlResource();
// 将当前类加到loadedResources集合中, 防止重复解析
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
// 此处用于判断接口中的方法是否是default修饰 或者是由于使用泛型生成的桥接方法
// 这两种类型的方法都不会进行处理
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
// 如果方法上含有@Select @SelectProvider 注解 但是没有指定 @ResultMap
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
下面对方法的细节进行介绍:
getAnnotationWrapper
该方法返回Optional<AnnotationWrapper>, AnnotationWrapper是方法上注解信息的封装, 而注解的范围由Collection<Class<? extends Annotation>> targetTypes参数进行限制. Method method参数用于反射获取方法注解.
targetTypes是所有需要处理的注解类的集合, 方法中的第二个参数用于在没有匹配的注解时是否抛出异常.
private Optional<AnnotationWrapper> getAnnotationWrapper(Method method, boolean errorIfNoMatch,
Collection<Class<? extends Annotation>> targetTypes) {
String databaseId = configuration.getDatabaseId();
// 1. 首先获取方法上, 所有在targetTypes范围中的注解
// 2. 之后根据上一步获取到的Annotation, 创建AnnotationWrapper对象
// 3. 最后组合为map结构, key为数据库厂商标识, value为AnnotationWrapper对象
// 如果出现重复的注解直接抛出异常
Map<String, AnnotationWrapper> statementAnnotations = targetTypes.stream()
.flatMap(x -> Arrays.stream(method.getAnnotationsByType(x))).map(AnnotationWrapper::new)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(AnnotationWrapper::getDatabaseId, x -> x, (existing, duplicate) -> {
throw new BuilderException(String.format("Detected conflicting annotations '%s' and '%s' on '%s'.",
existing.getAnnotation(), duplicate.getAnnotation(),
method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName()));
}));
// 之后的步骤是用于:
// 获取当前数据库厂商标识所支持的AnnotationWrapper
AnnotationWrapper annotationWrapper = null;
if (databaseId != null) {
annotationWrapper = statementAnnotations.get(databaseId);
}
// 如果没有取到 则获取没有配置数据库厂商标识的所有AnnotationWrapper
if (annotationWrapper == null) {
annotationWrapper = statementAnnotations.get("");
}
// 如果
if (errorIfNoMatch && annotationWrapper == null && !statementAnnotations.isEmpty()) {
// Annotations exist, but there is no matching one for the specified databaseId
throw new BuilderException(
String.format(
"Could not find a statement annotation that correspond a current database or default statement on method '%s.%s'. Current database id is [%s].",
method.getDeclaringClass().getName(), method.getName(), databaseId));
}
return Optional.ofNullable(annotationWrapper);
}
AnnotationWrapper 是mybatis sql映射注解信息的封装. 它包含三个成员变量:
- sql映射注解类: private final Annotation annotation;
- 数据库厂商标识: private final String databaseId;
- sql命令类型枚举(包括UNKNOWN, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH):
private final SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;
以上参数的初始化在构造器中完成. 即map(AnnotationWrapper::new). 下面是构造器的具体内容:
AnnotationWrapper(Annotation annotation) {
super();
this.annotation = annotation;
if (annotation instanceof Select) {
databaseId = ((Select) annotation).databaseId();
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.SELECT;
} else if (annotation instanceof Update) {
databaseId = ((Update) annotation).databaseId();
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.UPDATE;
} else if (annotation instanceof Insert) {
databaseId = ((Insert) annotation).databaseId();
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.INSERT;
} else if (annotation instanceof Delete) {
databaseId = ((Delete) annotation).databaseId();
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.DELETE;
} else if (annotation instanceof SelectProvider) {
databaseId = ((SelectProvider) annotation).databaseId();
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.SELECT;
} else if (annotation instanceof UpdateProvider) {
databaseId = ((UpdateProvider) annotation).databaseId();
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.UPDATE;
} else if (annotation instanceof InsertProvider) {
databaseId = ((InsertProvider) annotation).databaseId();
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.INSERT;
} else if (annotation instanceof DeleteProvider) {
databaseId = ((DeleteProvider) annotation).databaseId();
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.DELETE;
} else {
sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN;
if (annotation instanceof Options) {
databaseId = ((Options) annotation).databaseId();
} else if (annotation instanceof SelectKey) {
databaseId = ((SelectKey) annotation).databaseId();
} else {
databaseId = "";
}
}
}
parseResultMap
private String parseResultMap(Method method) {
Class<?> returnType = getReturnType(method);
// mybatis支持两种方式的结果映射注解 @Arg 或者 @Result
Arg[] args = method.getAnnotationsByType(Arg.class);
Result[] results = method.getAnnotationsByType(Result.class);
// 类型鉴别器 当某个字段值符合case中的值时使用该case的结果作为返回
// 可以参考 https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/sqlmap-xml.html 中 鉴别器一节
TypeDiscriminator typeDiscriminator = method.getAnnotation(TypeDiscriminator.class);
// 生成一个唯一的ResultMapId
String resultMapId = generateResultMapName(method);
applyResultMap(resultMapId, returnType, args, results, typeDiscriminator);
return resultMapId;
}
private String generateResultMapName(Method method) {
Results results = method.getAnnotation(Results.class);
// 如果@Results注解中指定了id这直接使用该类名+id作为结果
if (results != null && !results.id().isEmpty()) {
return type.getName() + "." + results.id();
}
// 否则: 使用方法参数类型拼接 作为后缀
StringBuilder suffix = new StringBuilder();
for (Class<?> c : method.getParameterTypes()) {
suffix.append("-");
suffix.append(c.getSimpleName());
}
// 如果没有参数 则使用-void 作为后缀
if (suffix.length() < 1) {
suffix.append("-void");
}
// 使用类名+方法名+后缀作为结果
return type.getName() + "." + method.getName() + suffix;
}
private void applyResultMap(String resultMapId, Class<?> returnType, Arg[] args, Result[] results, TypeDiscriminator discriminator) {
// 用于存放 @Arg 和 @Result 对应的 ResultMapping对象
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
// 生成@Arg注解对应的 ResultMapping对象
applyConstructorArgs(args, returnType, resultMappings);
// 生成@Result注解对应的 ResultMapping对象
applyResults(results, returnType, resultMappings);
// 生成鉴别器类 Discriminator
Discriminator disc = applyDiscriminator(resultMapId, returnType, discriminator);
// 创建ResultMap 并添加到configuration中的 Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps 中
assistant.addResultMap(resultMapId, returnType, null, disc, resultMappings, null);
// 鉴别器 根据字段值进行匹配对应的结果case后 之后同样会执行 applyConstructorArgs applyResults assistant.addResultMap
createDiscriminatorResultMaps(resultMapId, returnType, discriminator);
}
private void createDiscriminatorResultMaps(String resultMapId, Class<?> resultType, TypeDiscriminator discriminator) {
if (discriminator != null) {
for (Case c : discriminator.cases()) {
String caseResultMapId = resultMapId + "-" + c.value();
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
// issue #136
applyConstructorArgs(c.constructArgs(), resultType, resultMappings);
applyResults(c.results(), resultType, resultMappings);
// TODO add AutoMappingBehaviour
assistant.addResultMap(caseResultMapId, c.type(), resultMapId, null, resultMappings, null);
}
}
}
通过以上分析可知, mybatis支持使用@Result 以及 @Arg 进行构建结果映射对象.
鉴别器可以根据字段的值, 动态匹配不同的映射结果.
下面再看一下 assistant.addResultMap 方法:
public ResultMap addResultMap(
String id,
Class<?> type,
String extend,
Discriminator discriminator,
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings,
Boolean autoMapping) {
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
extend = applyCurrentNamespace(extend, true);
// 将extend对应的ResultMapping集合, 都添加到resultMappings中并且移除两者公共的.
if (extend != null) {
if (!configuration.hasResultMap(extend)) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Could not find a parent resultmap with id '" + extend + "'");
}
ResultMap resultMap = configuration.getResultMap(extend);
List<ResultMapping> extendedResultMappings = new ArrayList<>(resultMap.getResultMappings());
// 移除extendedResultMappings中含有的resultMappings的部分
extendedResultMappings.removeAll(resultMappings);
// 移除extendedResultMappings中含有resultMappings构造器映射的ResultMapping
// Remove parent constructor if this resultMap declares a constructor.
boolean declaresConstructor = false;
for (ResultMapping resultMapping : resultMappings) {
if (resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
declaresConstructor = true;
break;
}
}
if (declaresConstructor) {
extendedResultMappings.removeIf(resultMapping -> resultMapping.getFlags().contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR));
}
// 将移除干净后的extendedResultMappings 添加到resultMappings集合中
resultMappings.addAll(extendedResultMappings);
}
// 构建ResultMap对象并交给configuration进行管理
// addResultMap 会将ResultMap对象加入到Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps中并使用ResultMap的id作为key
ResultMap resultMap = new ResultMap.Builder(configuration, id, type, resultMappings, autoMapping)
.discriminator(discriminator)
.build();
configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);
return resultMap;
}
parseStatement
该方法用于将接口上的sql注解中的信息, 转换成MappedStatement类型, 并使用Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements管理已经解析过的statement.
在MappedStatement类中比较重要的类有:
StatementType statementType: sql语句的类型, 有STATEMENT(不进行预编译), PREPARED(预编译), CALLABLE(存储过程)SqlSource: 它提供了用于获取对sql语句的BoundSql的方法. BoundSql的sql参数为转换占位符后的sql语句String parameterMap, Class<?> parameterType: sql中参数的映射类型Class<?> resultType: 返回类String resultMap: 对应的结果resultMapIdKeyGenerator keyGenerator: key生成策略
void parseStatement(Method method) {
final Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
final LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
// 此处的getAnnotationWrapper方法逻辑同上,statementAnnotationTypes的注解范围为:
// Select.class, Update.class, Insert.class, Delete.class,
// SelectProvider.class, UpdateProvider.class, InsertProvider.class, DeleteProvider.class
getAnnotationWrapper(method, true, statementAnnotationTypes).ifPresent(statementAnnotation -> {
// SqlSource提供了getBoundSql方法, 用于获取BoundSql. BoundSql是sql注解(xml)的封装, 包含如下属性:
// sql: 经过转换后的sql字符串(预编译格式的, 而非原始的字符串, 已经将占位符进行处理)
// parameterMappings: 参数映射列表. List<ParameterMapping>类型. ParameterMapping类包含了参数的名称, javaType, jdbcType, 类型转换器等.
//
final SqlSource sqlSource = buildSqlSource(statementAnnotation.getAnnotation(), parameterTypeClass, languageDriver, method);
// SqlCommandType为枚举类型当生成AnnotationWrapper时 对不同的注解进行设置SqlCommandType的值.
// 比如:
// if (annotation instanceof Select) {
// databaseId = ((Select) annotation).databaseId();
// sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// }
final SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = statementAnnotation.getSqlCommandType();
final Options options = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Options.class).map(x -> (Options)x.getAnnotation()).orElse(null);
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
// 对于Insert和Update可以配置SelectKey注解用于生成主键, 这里进行KeyGenerator的实例化.
final KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) {
// first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else
SelectKey selectKey = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, SelectKey.class).map(x -> (SelectKey)x.getAnnotation()).orElse(null);
if (selectKey != null) {
keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method), languageDriver);
keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty();
} else if (options == null) {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
} else {
keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
keyProperty = options.keyProperty();
keyColumn = options.keyColumn();
}
} else {
keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
Integer fetchSize = null;
Integer timeout = null;
// 使用预编译类型的statement
StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
ResultSetType resultSetType = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
// 如果是select类型则支持使用缓存
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = !isSelect;
boolean useCache = isSelect;
// 如果有Options注解的配置 则进行后续处理, 覆盖默认的flushCache useCache fetchSize statementType resultSetType值
if (options != null) {
if (FlushCachePolicy.TRUE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = true;
} else if (FlushCachePolicy.FALSE.equals(options.flushCache())) {
flushCache = false;
}
useCache = options.useCache();
fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null; //issue #348
timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null;
statementType = options.statementType();
if (options.resultSetType() != ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {
resultSetType = options.resultSetType();
}
}
String resultMapId = null;
if (isSelect) {
ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class);
if (resultMapAnnotation != null) {
resultMapId = String.join(",", resultMapAnnotation.value());
} else {
resultMapId = generateResultMapName(method);
}
}
// 使用Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements管理已经解析过的statement
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
statementType,
sqlCommandType,
fetchSize,
timeout,
// ParameterMapID
null,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMapId,
getReturnType(method),
resultSetType,
flushCache,
useCache,
// TODO gcode issue #577
false,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
keyColumn,
statementAnnotation.getDatabaseId(),
languageDriver,
// ResultSets
options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null);
});
}
XMLMapperBuilder
mapper节点配置, 使用url或者resource属性都会使用该类进行解析xml配置.
相比较于MapperAnnotationBuilder, 由于xml不是java编译器所理解的东西. 因此需要对xml在加载的时候进行解析为相应的对象才能够使用. XPathParser就是一种通过xpath进行xml节点及属性获取的工具.
XMLMapperBuilder构造器为:
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
this.resource = resource;
}
parse
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
configurationElement方法用于解析mapper节点中的配置. 该方法的代码见下:
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
parameterMapElement方法用于解析parameterMap节点. 解析的结果会通过ParameterMap进行封装, id为该映射的唯一id, type为映射对应的java类型, parameterMappings为各个属性的映射信息, 每个属性的映射信息都是一个ParameterMapping对象. 最后该ParameterMap交给configuration的Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps进行管理.
resultMapElement方法用于解析resultMap节点, 该节点的定义见下(只粘贴了部分)
<!ELEMENT resultMap (constructor?,id*,result*,association*,collection*, discriminator?)>
<!ATTLIST resultMap
id CDATA #REQUIRED
type CDATA #REQUIRED
extends CDATA #IMPLIED
autoMapping (true|false) #IMPLIED
>
<!ELEMENT constructor (idArg*,arg*)>
<!ELEMENT id EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST id
property CDATA #IMPLIED
javaType CDATA #IMPLIED
column CDATA #IMPLIED
jdbcType CDATA #IMPLIED
typeHandler CDATA #IMPLIED
>
<!ELEMENT result EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST result
property CDATA #IMPLIED
javaType CDATA #IMPLIED
column CDATA #IMPLIED
jdbcType CDATA #IMPLIED
typeHandler CDATA #IMPLIED
>
譬如, xml中我们有如下的配置
<resultMap id="chatUserResultMap" type="chatUser">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="long" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="user_id" property="userId" javaType="long" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="room_id" property="roomId" javaType="long" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result column="message" property="message" javaType="string" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="type" property="type" javaType="messageTypeEnum" jdbcType="TINYINT" typeHandler="defaultEnumHandler"/>
<result column="status" property="status" javaType="statusEnum" jdbcType="TINYINT" typeHandler="defaultEnumHandler"/>
<result column="create_time" property="createTime" javaType="date" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"/>
<result column="update_time" property="updateTime" javaType="date" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"/>
</resultMap>
下面来分析解析的代码, 首先获取结果映射对应的类Class<?> typeClass. 优先从DTD中定义的type属性上获取, 否则获取ofType, resultType, javaType属性, 当然后者在上面的规范中并不存在, 但使用者仍旧可以配置.
for循环遍历resultChildren, 用于处理resultMap的子节点, 并将每个子节点封装为ResultMapping对象.
extends属性表示当前resultMap继承的父resultMap映射配置. 在ResultMapResolver的resolve方法中会获取所继承的resultMap, 并移除相同的ResultMapping得到最终的List<ResultMapping>, 并构建ResultMap对象. 交由configuration的Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps管理.
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings, Class<?> enclosingType) {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
if (typeClass == null) {
typeClass = inheritEnclosingType(resultMapNode, enclosingType);
}
Discriminator discriminator = null;
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>(additionalResultMappings);
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}
sqlElement
sqlElement是用于解析sql片段的方法.
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) {
sqlFragments.put(id, context);
}
}
}
需要注意的是, sql片段交给的XMLMapperBuilder类的Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments进行管理. 我们可以猜测它的意图在于后续解析sql语句中遇到了include引入sql片段时, 直接根据id获取相应的sql片段节点对象.
buildStatementFromContext
该方法对select|insert|update|delete 这4种节点进行处理.
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
每个sql节点都会创建一个XMLStatementBuilder对象, 并调用parseStatementNode方法进行解析.
与java注解方式类似,同样需要构建MappedStatement对象,并放入Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements中,但由于xml中可以使用sql片段因此需要使用XMLIncludeTransformer对sql片段进行处理。
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
if (resultSetTypeEnum == null) {
resultSetTypeEnum = configuration.getDefaultResultSetType();
}
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
像是如下的代码:
<sql id="chatUserColumns">
<trim>
${alias}.id,
${alias}.user_id,
${alias}.room_id,
${alias}.message,
${alias}.`type`,
${alias}.status,
${alias}.create_time,
${alias}.update_time
</trim>
</sql>
<select id="selectChatUserList" resultMap="chatUserResultMap">
select
<include refid="chatUserColumns">
<property name="alias" value="cu"/>
</include>
from chat_user cu
where cu.user_id = #{userId}
</select>
执行过include替换之后, 会变成下图中的结果. 之后进行sqlSource的创建等步骤与之前注解方式相差不大.
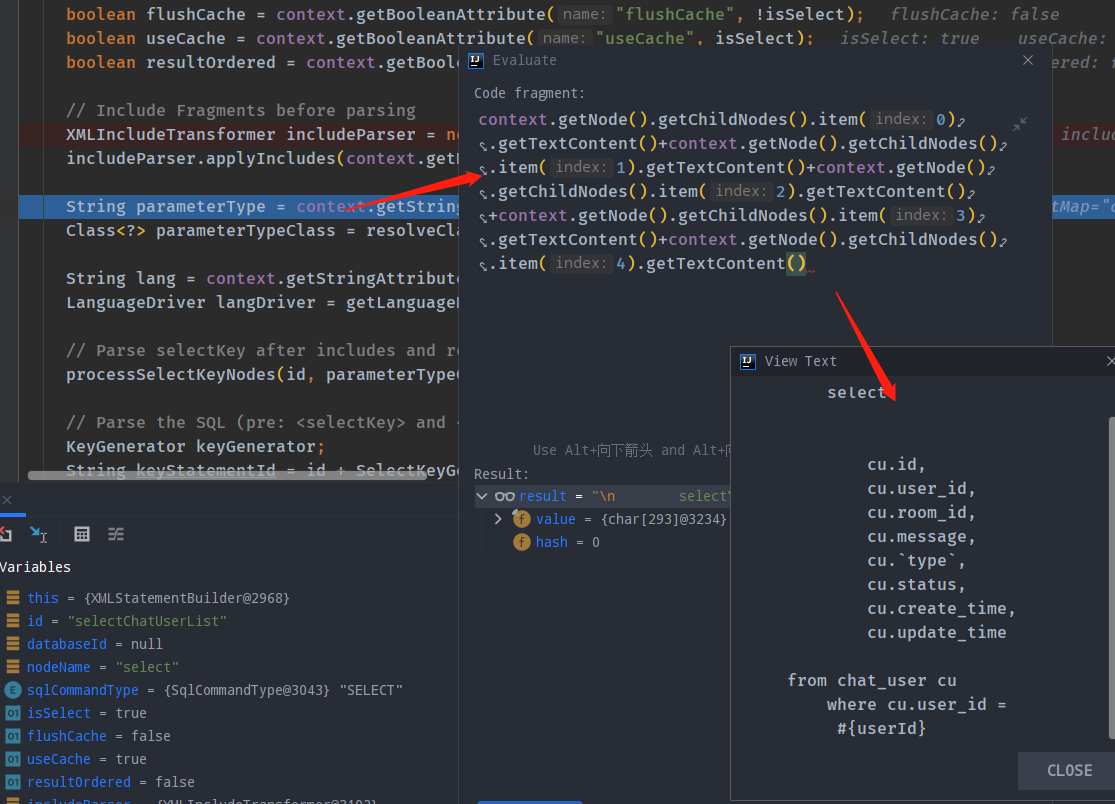
后续步骤
解析过当前的resource后, Set<String> loadedResources会记录当前的resource.
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
这三个方法用于处理之前解析过程中出现异常没有完成解析的对象.





